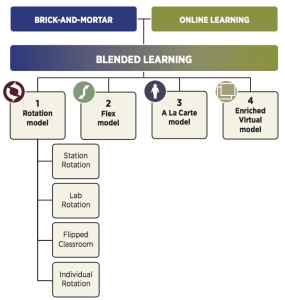
Blended Learning Models
Blended Learning is the combination of both traditional brick-and-mortar and online instruction in which "teachers create multiple pathways for student success. Students have some element of control in the time, place, path, and/or pace of learning."
--International Association for K-12 Online Learning (iNACOL)
Rotation Model
a. Station Rotation — a course or subject in which students experience the Rotation model within a contained classroom or group of classrooms. The Station Rotation model differs from the Individual Rotation model because students rotate through all of the stations, not only those on their custom schedules.
b. Lab Rotation — a course or subject in which students rotate to a computer lab for the online-learning station.
c. Flipped Classroom — a course or subject in which students participate in online learning off-site in place of traditional homework and then attend the brick-and-mortar school for face-to-face, teacher-guided practice or projects. The primary delivery of content and instruction is online, which differentiates a Flipped Classroom from students who are merely doing homework practice online at night.
d. Individual Rotation — a course or subject in which each student has an individualized playlist and does not necessarily rotate to each available station or modality. An algorithm or teacher(s) sets individual student schedules.
Flex Model
— a course or subject in which online learning is the backbone of student learning, even if it directs students to offline activities at times. Students move on an individually customized, fluid schedule among learning modalities. The teacher of record is on-site, and students learn mostly on the brick-and-mortar campus, except for any homework assignments. The teacher of record or other adults provide face-to-face support on a flexible and adaptive as-needed basis through activities such as small-group instruction, group projects, and individual tutoring. Some implementations have substantial face-to-face support, whereas others have minimal support.
A La Carte Model
— a course that a student takes entirely online to accompany other experiences that the student is having at a brick-and-mortar school or learning center. The teacher of record for the A La Carte course is the online teacher. Students may take the A La Carte course either on the brick-and-mortar campus or off-site. This differs from full-time online learning because it is not a whole-school experience. Students take some courses A La Carte and others face-to-face at a brick-and-mortar campus.
Enriched Virtual Model
— a course or subject in which students have required face-to-face learning sessions with their teacher of record and then are free to complete their remaining coursework remote from the face-to-face teacher. Online learning is the backbone of student learning when the students are located remotely. The same person generally serves as both the online and face-to-face teacher. Many Enriched Virtual programs began as full-time online schools and then developed blended programs to provide students with brick-and-mortar school experiences. The Enriched Virtual model differs from the Flipped Classroom because in Enriched Virtual programs, students seldom meet face-to-face with their teachers every weekday. It differs from a fully online course because face-to-face learning sessions are more than optional office hours or social events; they are required.
Source: Blended Learning Definitions Michael B. Horn and Heather Staker, Blended: Using Disruptive Innovation to Improve Schools (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 2014).